JULY 12 — Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR), Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) and Environmental, Social and Governance (ESG) are increasingly significant in today’s business world.
These frameworks shape how businesses, governments and societies tackle global challenges, such as climate change and poverty.
In Malaysia, they are key to achieving sustainability, working together to drive long-term positive impact.
CSR as a pathway to sustainability
Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) is a business model where companies voluntarily integrate social, environmental and ethical concerns into their operations.
CSR goes beyond profit-making by contributing positively to society and supporting sustainable development. It includes charity work, environmental initiatives, community development and employee welfare.
The key aspect of CSR is its voluntary nature, whereby companies engage in these practices because they align with their values, not due to legal obligations.
In Malaysia, CSR has become a crucial part of corporate culture, with businesses contributing to national goals on education, healthcare and environmental conservation, supporting the country’s broader sustainability objectives.
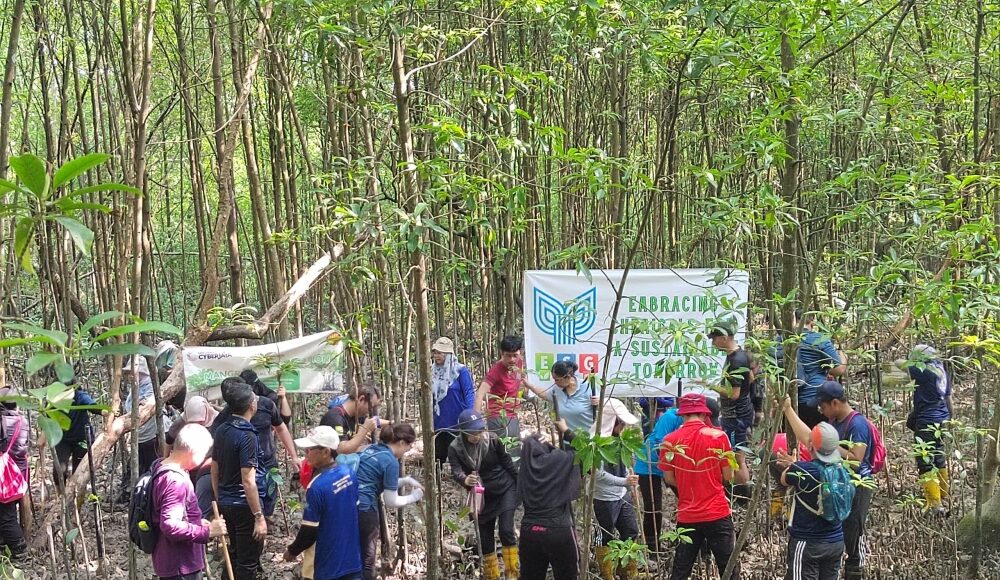
Employees of agrochemical company Ancom Nylex and its subsidiaries take part in a tree planting exercise at Taman Rekreasi Paya Bakau Kampung Sijangkang, Selangor on February 15, 2025. — Picture courtesy of Ancom Nylex Bhd
The SDGs: A global framework for achieving sustainability
The Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), adopted by the United Nations in 2015, consist of 17 global objectives aimed at addressing issues such as poverty, inequality, climate change and environmental degradation by 2030.
These goals serve as a universal framework for governments, businesses and civil society to collaborate and drive global sustainability.
In Malaysia, the SDGs have been integrated into national policies, aligning efforts to improve healthcare, reduce poverty and combat climate change.
Companies aligning their operations with the SDGs help achieve these global goals, driving long-term economic growth while promoting environmental protection and social equity.
By contributing to SDGs, businesses also take important steps toward realising a more sustainable future for the country and the world.
ESG: A tool for sustainable business practices
ESG (Environmental, Social and Governance) is a set of criteria used by investors to evaluate a company’s sustainability practices and ethical impact.
ESG focuses on three core areas: environmental (e.g. carbon emissions, waste management), social (e.g. labour practices, community engagement) and governance (e.g. board structure, executive compensation).
Unlike CSR, which is internally driven and voluntary, ESG provides measurable and standardised metrics that allow investors to assess a company’s performance in these areas.
As ESG metrics are increasingly incorporated into investment decisions, companies with strong ESG performance are more likely to attract responsible investment, manage sustainability risks and align with global sustainability goals.
In Malaysia, ESG disclosures have become mandatory for publicly listed companies, marking a significant shift toward greater transparency in corporate sustainability and reinforcing its role in achieving national and global sustainability targets.
Sustainability as the overarching goal
Sustainability serves as the guiding philosophy that connects CSR, SDGs and ESG.
It refers to meeting present needs without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own.
Sustainability encompasses environmental, economic and social dimensions, ensuring that development is both inclusive and environmentally sound.
In business, sustainability requires companies to develop long-term strategies that reduce their environmental impact, support social equity and promote economic prosperity. Sustainability is the framework within which CSR, SDGs and ESG operate.
While each of these frameworks plays a role, they all contribute to the overarching goal of sustainability, ensuring that businesses and nations work toward a balanced future that benefits both people and the planet.
How CSR, SDGs and ESG contribute to sustainability in Malaysia
CSR, SDGs and ESG are not isolated concepts. Rather, they are interconnected and complementary pathways to achieving sustainability.
CSR initiatives directly contribute to the SDGs by addressing social and environmental challenges, such as health, education and environmental protection.
For example, many Malaysian businesses are already implementing CSR programmes aligned with SDG 8 (Decent work and economic growth), which support initiatives such as youth skill development and job creation for underserved communities or SDG 4 (Quality education), which focuses on enhancing community education programmes.
At the same time, ESG metrics provide businesses with the tools to measure and manage their contributions to sustainability, aligning corporate actions with SDGs.
ESG disclosures help companies assess and report their performance on key sustainability indicators such as climate action (SDG 13), gender equality (SDG 5) and responsible consumption (SDG 12).
Companies that perform well in ESG reporting are more likely to contribute to SDG targets, such as reducing carbon emissions and promoting fair labour practices.
Sustainability, as the broader framework, encompasses all of these efforts, ensuring that CSR, ESG and SDGs are not just individual objectives but are interconnected components of a holistic approach to achieving long-term societal and environmental well-being.
In Malaysia, sustainability is at the core of national policy, guiding efforts to reduce carbon emissions, tackle resource depletion and address social inequality.
The government’s commitment to achieving carbon neutrality by 2050 is a key example of how Malaysia is integrating sustainability into its development agenda.
The Bursa Malaysia ESG Reporting Platform and the National Sustainability Reporting Framework (NSRF) play important roles in helping Malaysia integrate CSR, SDGs and ESG to achieve sustainability.
The ESG platform, launched in December 2023, requires public listed companies to disclose their ESG performance, ensuring alignment with the SDGs and promoting transparency in corporate sustainability.
The NSRF, introduced in September 2024, further strengthens this by guiding companies to adopt standardised sustainability reporting aligned with international standards such as the IFRS Sustainability Disclosure Standards.
These frameworks foster accountability, enhance risk management and encourage responsible investment, providing clear benchmarks for measuring progress towards Malaysia’s sustainable development.
In conclusion, CSR, SDGs and ESG are essential drivers of sustainability in Malaysia. With the dedicated ESG Reporting Platform and the NSRF, they collectively support businesses in aligning their operations with global sustainability goals, ensuring long-term growth and societal well-being.
* Dalilawati Zainal is with the Department of Accounting, Faculty of Business and Economics, Universiti Malaya. She may be contacted at [email protected]
** This is the personal opinion of the writer or publication and does not necessarily represent the views of Malay Mail.